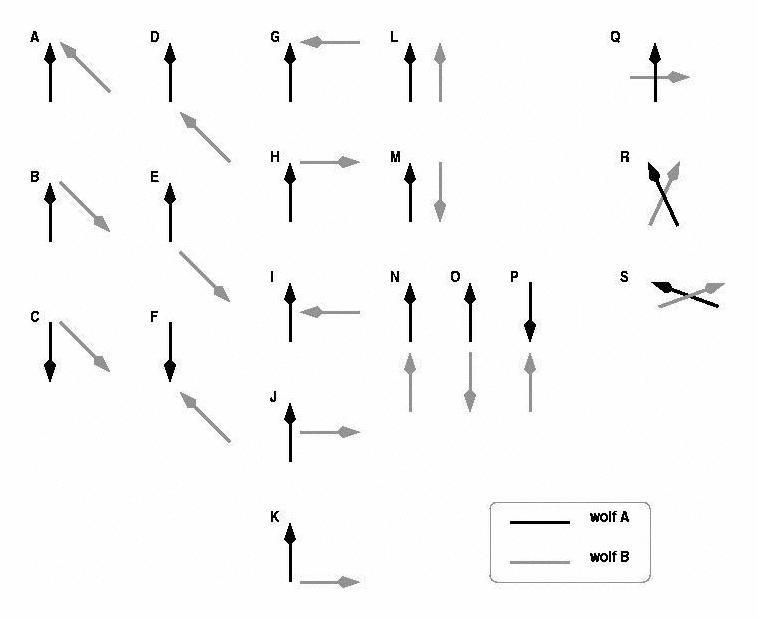
In this coding section, you must determine which of the configurations of arrows in the following chart best represents the mutual position of the pair of wolves you are coding.
To complete this coding section, please follow the instructions below:
Before moving on to the next key, you are encouraged to review the instructions and confirm your choices. If you are satisfied with your codes, please continue here

| A | Heads converge at a 45° angle. | K | Tails converge at a 90° angle. |
| B | Head of one wolf converges with tail of other wolf at a 45° angle. | L | Wolves are positioned side-by-side with heads parallel. |
| C | Tails converge at a 45° angle. | M | Wolves are positioned side-by-side with heads parallel to tails. |
| D | Head of one wolf converges with tail of other wolf at a 135° angle. | N | Head of one wolf approaches tail of other wolf such that their bodies from a straight line. (See Following and Anal Oriented Investigation). |
| E | Tails converge at a 135° angle. | O | Tail of one wolf approaches tail of other wolf such that their bodies from a straight line and wolves are facing directly away from each other. |
| F | Heads converge at a 135° angle. | P | Head of one wolf approaches head of other wolf such that their bodies form a straight line and wolves are facing each other. |
| G | Heads converge at a 90° angle. | Q | One wolf stands over midsection of other wolf's back at a 90° angle. |
| H | Head of one wolf converges with tail of other wolf at a 90° angle. | R | One wolf stands over other wolf such that their heads diverge at a 45° angle (i.e. heads are closer together). |
| I | Head of one wolf intercepts midsection of other wolf's flank at a 90° angle (T-Formation). | S | One wolf stands over other wolf such that their heads diverge at a 135° angle (i.e. heads are further apart). |
| J | Tail of one wolf intercepts midsection of other wolf's flank at a 90° angle (T- Formation). | Z | Unable to determine mutual orientation of wolves . |